Publications & Patents
Please reach out if you need a preprint of a paper not available here.
Contents
- Featured Publications
- Theses
- Journal Articles
- Conference and Workshop Papers
- Technical Reports
- Patents
Featured Publications 
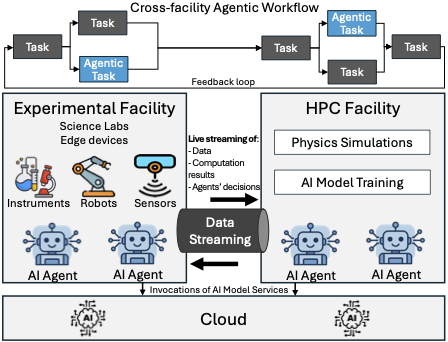 | PROV-AGENT: Unified Provenance for Tracking AI Agent Interactions in Agentic Workflows R. Souza, A. Gueroudji, S. DeWitt, D. Rosendo, T. Ghosal, R. Ross, P. Balaprakash, and R.F.d. Silva 2025 IEEE International Conference on eScience (eScience), 2025. [F1][doi] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Large Language Models (LLMs) and other foundation models are increasingly used as the core of AI agents. In agentic workflows, these agents plan tasks, interact with humans and peers, and influence scientific outcomes across federated and heterogeneous environments. However, agents can hallucinate or reason incorrectly, propagating errors when one agent's output becomes another's input. Thus, assuring that agents' actions are transparent, traceable, reproducible, and reliable is critical to assess hallucination risks and mitigate their workflow impacts. While provenance techniques have long supported these principles, existing methods fail to capture and relate agent-centric metadata such as prompts, responses, and decisions with the broader workflow context and downstream outcomes. In this paper, we introduce PROV-AGENT, a provenance model that extends W3C PROV and leverages the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and data observability to integrate agent interactions into end-to-end workflow provenance. Our contributions include: (1) a provenance model tailored for agentic workflows, (2) a near real-time, open-source system for capturing agentic provenance, and (3) a cross-facility evaluation spanning edge, cloud, and HPC environments, demonstrating support for critical provenance queries and agent reliability analysis. [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_prov_agent_2025,
author = {Renan Souza and Amal Gueroudji and Stephen DeWitt and Daniel Rosendo and Tirthankar Ghosal and Robert Ross and Prasanna Balaprakash and Rafael Ferreira da Silva},
title = {PROV-AGENT: Unified Provenance for Tracking {AI} Agent Interactions in Agentic Workflows},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on e-Science},
year = {2025},
booktitle = { 2025 IEEE International Conference on eScience (eScience) },
doi = {10.1109/eScience65000.2025.00093},
location = {Chicago, U.S.A.},
pdf = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2508.02866},
publisher = {IEEE},
keywords = {Artificial Intelligence, Provenance, Machine Learning, AI workflows, ML workflows, Responsible AI, Trustworthy AI, Reproducibility, AI Lifecycle, Energy-efficient AI},
abstract = {Large Language Models (LLMs) and other foundation models are increasingly used as the core of AI agents. In agentic workflows, these agents plan tasks, interact with humans and peers, and influence scientific outcomes across federated and heterogeneous environments. However, agents can hallucinate or reason incorrectly, propagating errors when one agent's output becomes another's input. Thus, assuring that agents' actions are transparent, traceable, reproducible, and reliable is critical to assess hallucination risks and mitigate their workflow impacts. While provenance techniques have long supported these principles, existing methods fail to capture and relate agent-centric metadata such as prompts, responses, and decisions with the broader workflow context and downstream outcomes. In this paper, we introduce PROV-AGENT, a provenance model that extends W3C PROV and leverages the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and data observability to integrate agent interactions into end-to-end workflow provenance. Our contributions include: (1) a provenance model tailored for agentic workflows, (2) a near real-time, open-source system for capturing agentic provenance, and (3) a cross-facility evaluation spanning edge, cloud, and HPC environments, demonstrating support for critical provenance queries and agent reliability analysis.}
} |
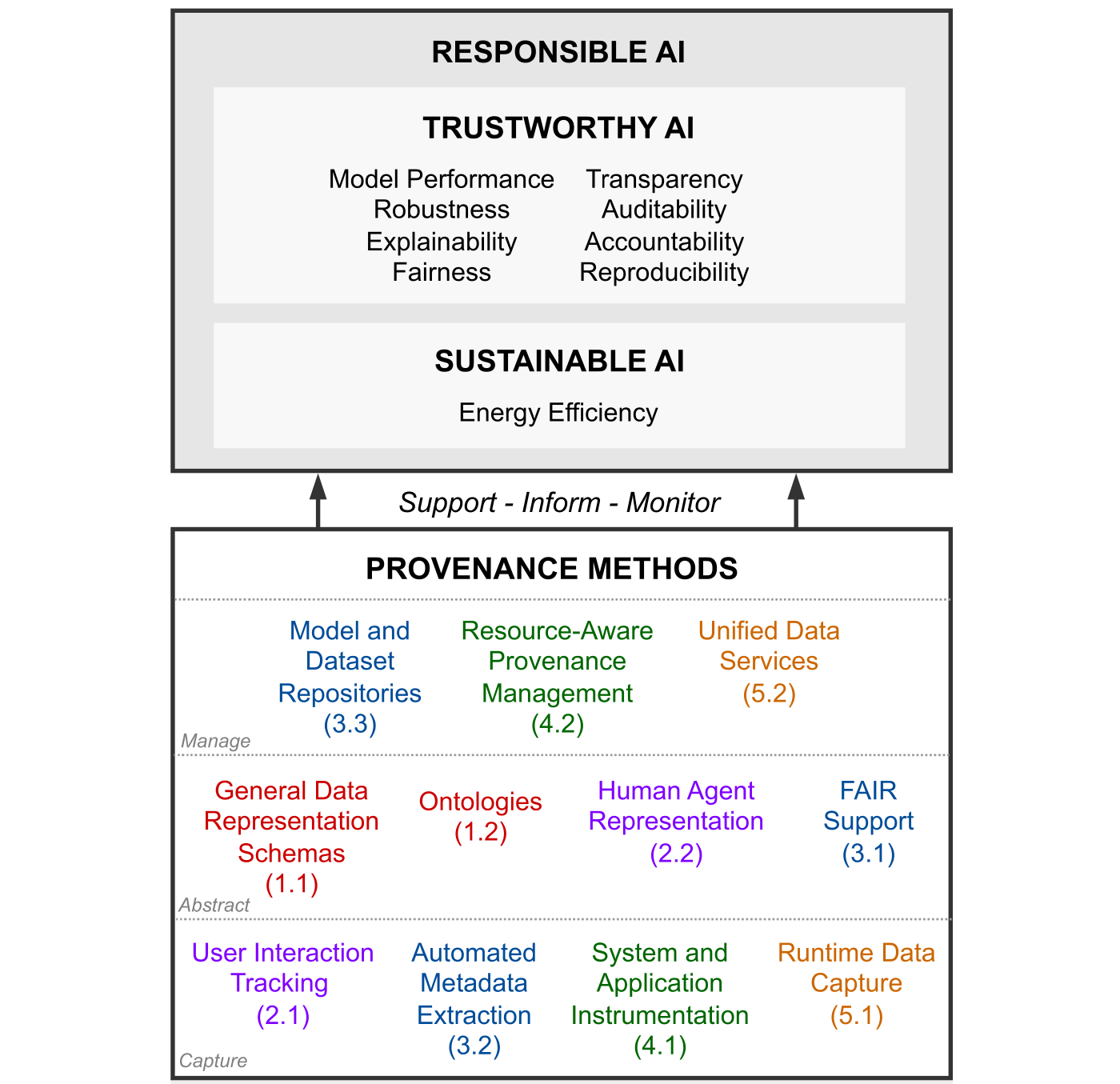 | Workflow Provenance in the Computing Continuum for Responsible, Trustworthy, and Energy-Efficient AI R. Souza, S. Caino-Lores, M. Coletti, T.J. Skluzacek, A. Costan, F. Suter, M. Mattoso, and R.F.d. Silva IEEE International Conference on e-Science, 2024. [F2][doi] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. As Artificial Intelligence (AI) becomes more pervasive in our society, it is crucial to develop, deploy, and assess Responsible and Trustworthy AI (RTAI) models, i.e., those that consider not only accuracy but also other aspects, such as explainability, fairness, and energy efficiency. Workflow provenance data have historically enabled critical capabilities towards RTAI. Provenance data derivation paths contribute to responsible workflows through transparency in tracking artifacts and resource consumption. Provenance data are well-known for their trustworthiness, helping explainability, reproducibility, and accountability. However, there are complex challenges to achieving RTAI, which are further complicated by the heterogeneous infrastructure in the computing continuum (Edge-Cloud-HPC) used to develop and deploy models. As a result, a significant research and development gap remains between workflow provenance data management and RTAI. In this paper, we present a vision of the pivotal role of workflow provenance in supporting RTAI and discuss related challenges. We present a schematic view of the relationship between RTAI and provenance, and highlight open research directions. [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_rtai_2024,
author = {Renan Souza and Silvina Caino-Lores and Mark Coletti and Tyler J. Skluzacek and Alexandru Costan and Frederic Suter and Marta Mattoso and Rafael Ferreira da Silva},
title = {Workflow Provenance in the Computing Continuum for Responsible, Trustworthy, and Energy-Efficient {AI}},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on e-Science},
year = {2024},
location = {Osaka, Japan},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1109/e-Science62913.2024.10678731},
pdf = {https://hal.science/hal-04902079v1/document},
publisher = {IEEE},
keywords = {Artificial Intelligence, Provenance, Machine Learning, AI workflows, ML workflows, Responsible AI, Trustworthy AI, Reproducibility, AI Lifecycle, Energy-efficient AI},
abstract = {As Artificial Intelligence (AI) becomes more pervasive in our society, it is crucial to develop, deploy, and assess Responsible and Trustworthy AI (RTAI) models, i.e., those that consider not only accuracy but also other aspects, such as explainability, fairness, and energy efficiency. Workflow provenance data have historically enabled critical capabilities towards RTAI. Provenance data derivation paths contribute to responsible workflows through transparency in tracking artifacts and resource consumption. Provenance data are well-known for their trustworthiness, helping explainability, reproducibility, and accountability. However, there are complex challenges to achieving RTAI, which are further complicated by the heterogeneous infrastructure in the computing continuum (Edge-Cloud-HPC) used to develop and deploy models. As a result, a significant research and development gap remains between workflow provenance data management and RTAI. In this paper, we present a vision of the pivotal role of workflow provenance in supporting RTAI and discuss related challenges. We present a schematic view of the relationship between RTAI and provenance, and highlight open research directions.}
} |
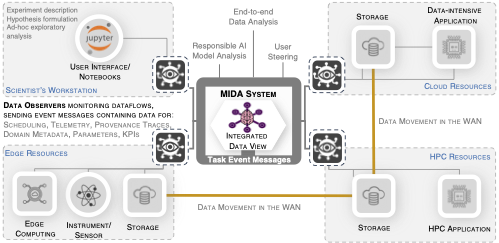 | Towards Lightweight Data Integration using Multi-workflow Provenance and Data Observability R. Souza, T.J. Skluzacek, S.R. Wilkinson, M. Ziatdinov, and R.F.d. Silva IEEE International Conference on e-Science, 2023. [F3][doi] [online] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Modern large-scale scientific discovery requires multidisciplinary collaboration across diverse computing facilities, including High Performance Computing (HPC) machines and the Edge-to-Cloud continuum. Integrated data analysis plays a crucial role in scientific discovery, especially in the current AI era, by enabling Responsible AI development, FAIR, Reproducibility, and User Steering. However, the heterogeneous nature of science poses challenges such as dealing with multiple supporting tools, cross-facility environments, and efficient HPC execution. Building on data observability, adapter system design, and provenance, we propose MIDA: an approach for lightweight runtime Multi-workflow Integrated Data Analysis. MIDA defines data observability strategies and adaptability methods for various parallel systems and machine learning tools. With observability, it intercepts the dataflows in the background without requiring instrumentation while integrating domain, provenance, and telemetry data at runtime into a unified database ready for user steering queries. We conduct experiments showing end-to-end multi-workflow analysis integrating data from Dask and MLFlow in a real distributed deep learning use case for materials science that runs on multiple environments with up to 276 GPUs in parallel. We show near-zero overhead running up to 100,000 tasks on 1,680 CPU cores on the Summit supercomputer. [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza2023towards,
title={Towards Lightweight Data Integration using Multi-workflow Provenance and Data Observability},
author={Souza, Renan and Skluzacek, Tyler J and Wilkinson, Sean R and Ziatdinov, Maxim and da Silva, Rafael Ferreira},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on e-Science},
doi={10.1109/e-Science58273.2023.10254822},
url={https://doi.org/10.1109/e-Science58273.2023.10254822},
pdf={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2308.09004.pdf},
year={2023},
abstract={Modern large-scale scientific discovery requires multidisciplinary collaboration across diverse computing facilities, including High Performance Computing (HPC) machines and the Edge-to-Cloud continuum. Integrated data analysis plays a crucial role in scientific discovery, especially in the current AI era, by enabling Responsible AI development, FAIR, Reproducibility, and User Steering. However, the heterogeneous nature of science poses challenges such as dealing with multiple supporting tools, cross-facility environments, and efficient HPC execution. Building on data observability, adapter system design, and provenance, we propose MIDA: an approach for lightweight runtime Multi-workflow Integrated Data Analysis. MIDA defines data observability strategies and adaptability methods for various parallel systems and machine learning tools. With observability, it intercepts the dataflows in the background without requiring instrumentation while integrating domain, provenance, and telemetry data at runtime into a unified database ready for user steering queries. We conduct experiments showing end-to-end multi-workflow analysis integrating data from Dask and MLFlow in a real distributed deep learning use case for materials science that runs on multiple environments with up to 276 GPUs in parallel. We show near-zero overhead running up to 100,000 tasks on 1,680 CPU cores on the Summit supercomputer.}
} |
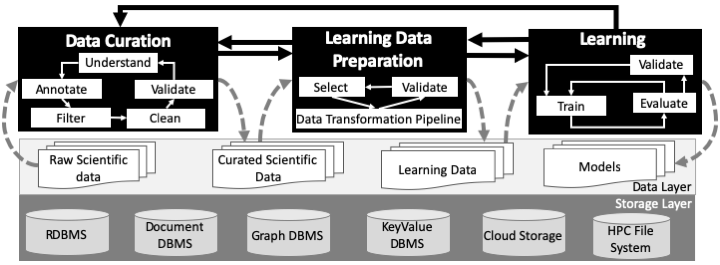 | Workflow Provenance in the Lifecycle of Scientific Machine Learning R. Souza, L.G. Azevedo, V. Lourenço, E. Soares, R. Thiago, R. Brandão, D. Civitarese, E.V. Brazil, M. Moreno, P. Valduriez, M. Mattoso, R. Cerqueira, and M.A.S. Netto Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2021. [F4][doi] [online] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Machine Learning (ML) has already fundamentally changed several businesses. More recently, it has also been profoundly impacting the computational science and engineering domains, like geoscience, climate science, and health science. In these domains, users need to perform comprehensive data analyses combining scientific data and ML models to provide for critical requirements, such as reproducibility, model explainability, and experiment data understanding. However, scientific ML is multidisciplinary, heterogeneous, and affected by the physical constraints of the domain, making such analyses even more challenging. In this work, we leverage workflow provenance techniques to build a holistic view to support the lifecycle of scientific ML. We contribute with (i) characterization of the lifecycle and taxonomy for data analyses; (ii) design principles to build this view, with a W3C PROV compliant data representation and a reference system architecture; and (iii) lessons learned after an evaluation in an Oil \& Gas case using an HPC cluster with 393 nodes and 946 GPUs. The experiments show that the principles enable queries that integrate domain semantics with ML models while keeping low overhead (<1\%), high scalability, and an order of magnitude of query acceleration under certain workloads against without our representation. [bibtex]@article{asouza2020workflow,
title={Workflow Provenance in the Lifecycle of Scientific Machine Learning},
author={Souza, Renan and G. Azevedo, Leonardo and Lourenço, Vítor and Soares, Elton and Thiago, Raphael and Brandão, Rafael and Civitarese, Daniel and Vital Brazil, Emilio and Moreno, Marcio and Valduriez, Patrick and Mattoso, Marta and Cerqueira, Renato and A. S. Netto, Marco},
year={2021},
abstract={Machine Learning (ML) has already fundamentally changed several businesses. More recently, it has also been profoundly impacting the computational science and engineering domains, like geoscience, climate science, and health science. In these domains, users need to perform comprehensive data analyses combining scientific data and ML models to provide for critical requirements, such as reproducibility, model explainability, and experiment data understanding. However, scientific ML is multidisciplinary, heterogeneous, and affected by the physical constraints of the domain, making such analyses even more challenging. In this work, we leverage workflow provenance techniques to build a holistic view to support the lifecycle of scientific ML.
We contribute with (i) characterization of the lifecycle and taxonomy for data analyses; (ii) design principles to build this view, with a W3C PROV compliant data representation and a reference system architecture; and (iii) lessons learned after an evaluation in an Oil \& Gas case using an HPC cluster with 393 nodes and 946 GPUs.
The experiments show that the principles enable queries that integrate domain semantics with ML models while keeping low overhead (<1\%), high scalability, and an order of magnitude of query acceleration under certain workloads against without our representation.},
url={https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.6544},
doi={10.1002/cpe.6544},
pdf={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.00330.pdf},
journal={Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience},
pages={1--21},
volume={e6544}
} |
Theses 
| Supporting User Steering in Large-scale Workflows with Provenance Data R. Souza COPPE/Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Ph.D. Thesis, 2019. [T1][online] [pdf] [bibtex]@article{souza_phd_2019,
title={Supporting User Steering in Large-scale Workflows with Provenance Data},
author={Souza, Renan},
year={2019},
journal={COPPE/Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Ph.D. Thesis},
url = {https://www.cos.ufrj.br/index.php/en/publicacoes-pesquisa/details/20/2940},
pdf = {https://www.cos.ufrj.br/uploadfile/publicacao/2940.pdf}
} |
| Controlling the Parallel Execution of Workflows Relying on a Distributed Database R. Souza COPPE/Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, M.Sc. Thesis, 2015. [T2][online] [pdf] [bibtex]@article{souza_msc_2015,
title={Controlling the Parallel Execution of Workflows Relying on a Distributed Database},
author={Souza, Renan},
year={2015},
journal={COPPE/Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, M.Sc. Thesis},
url = {https://www.cos.ufrj.br/index.php/pt-BR/publicacoes-pesquisa/details/15/2562},
pdf = {https://www.cos.ufrj.br/uploadfile/publicacao/2562.pdf}
} |
| Linked Open Data Publication Strategies: An Application in Network Performance Data (in pt) R. Souza DCC/Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, B.Sc. Thesis, 2013. [T3][pdf] [bibtex]@article{souza_bsc_2015,
title={Linked Open Data Publication Strategies: An Application in Network Performance Data (in pt)},
author={Souza, Renan},
year={2013},
journal={DCC/Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, B.Sc. Thesis},
pdf = {https://renansouza.org/data/papers/souza-bsc-thesis.pdf}
} |
Journal Articles 
| Toward a Persistent Event-Streaming System for High-Performance Computing Applications M. Dorier, A. Gueroudji, V. Hayot-Sasson, H. Nguyen, S. Ockerman, R. Souza, T. Bicer, H. Pan, P. Carns, K. Chard, and others Frontiers in High Performance Computing, 2025. [J1][doi] [online] [pdf] [bibtex]@article{dorier2025toward,
title={Toward a Persistent Event-Streaming System for High-Performance Computing Applications},
author={Dorier, Matthieu and Gueroudji, Amal and Hayot-Sasson, Valerie and Nguyen, Hai and Ockerman, Seth and Souza, Renan and Bicer, Tekin and Pan, Haochen and Carns, Philip and Chard, Kyle and others},
journal={Frontiers in High Performance Computing},
volume={3},
pdf={https://public-pages-files-2025.frontiersin.org/journals/high-performance-computing/articles/10.3389/fhpcp.2025.1638203/pdf},
doi={10.3389/fhpcp.2025.1638203},
url={https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/high-performance-computing/articles/10.3389/fhpcp.2025.1638203/abstract},
year={2025},
publisher={Frontiers in High Performance Computing},
keywords={HPC, I/O, Streaming, Mochi, Mofka, Kafka, Redpanda}
} |
| Distributed In-memory Data Management for Workflow Executions R. Souza, V. Silva, A.A.B. Lima, D. Oliveira, P. Valduriez, and M. Mattoso PeerJ Computer Science, 2021. [J2][doi] [online] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Complex scientific experiments from various domains are typically modeled as workflows and executed on large-scale machines using a Parallel Workflow Management System (WMS). Since such executions usually last for hours or days, some WMSs provide user steering support, i.e., they allow users to run data analyses and, depending on the results, adapt the workflows at runtime. A challenge in the parallel execution control design is to manage workflow data for efficient executions while enabling user steering support. Data access for high scalability is typically transaction-oriented, while for data analysis, it is online analytical-oriented so that managing such hybrid workloads makes the challenge even harder. In this work, we present SchalaDB, an architecture with a set of design principles and techniques based on distributed in-memory data management for efficient workflow execution control and user steering. We propose a distributed data design for scalable workflow task scheduling and high availability driven by a parallel and distributed in-memory DBMS. To evaluate our proposal, we develop d-Chiron, a WMS designed according to SchalaDB's principles. We carry out an extensive experimental evaluation on an HPC cluster with up to 960 computing cores. Among other analyses, we show that even when running data analyses for user steering, SchalaDB's overhead is negligible for workloads composed of hundreds of concurrent tasks on shared data. Our results encourage workflow engine developers to follow a parallel and distributed data-oriented approach not only for scheduling and monitoring but also for user steering. [bibtex]@article{souza_distributed_2021,
author={Souza, R. and Silva, V. and Lima, A. A. B. and Oliveira, D. and Valduriez, P. and Mattoso, M.},
journal={PeerJ Computer Science},
title={Distributed In-memory Data Management for Workflow Executions},
year={2021},
pdf={https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2105/2105.04720.pdf},
url={https://peerj.com/articles/cs-527/},
doi={10.7717/peerj-cs.527},
pages={1--30},
volume={7},
abstract={Complex scientific experiments from various domains are typically modeled as workflows and executed on large-scale machines using a Parallel Workflow Management System (WMS). Since such executions usually last for hours or days, some WMSs provide user steering support, i.e., they allow users to run data analyses and, depending on the results, adapt the workflows at runtime. A challenge in the parallel execution control design is to manage workflow data for efficient executions while enabling user steering support. Data access for high scalability is typically transaction-oriented, while for data analysis, it is online analytical-oriented so that managing such hybrid workloads makes the challenge even harder. In this work, we present SchalaDB, an architecture with a set of design principles and techniques based on distributed in-memory data management for efficient workflow execution control and user steering. We propose a distributed data design for scalable workflow task scheduling and high availability driven by a parallel and distributed in-memory DBMS. To evaluate our proposal, we develop d-Chiron, a WMS designed according to SchalaDB's principles. We carry out an extensive experimental evaluation on an HPC cluster with up to 960 computing cores. Among other analyses, we show that even when running data analyses for user steering, SchalaDB's overhead is negligible for workloads composed of hundreds of concurrent tasks on shared data. Our results encourage workflow engine developers to follow a parallel and distributed data-oriented approach not only for scheduling and monitoring but also for user steering.}
} |
| Workflow Provenance in the Lifecycle of Scientific Machine Learning R. Souza, L.G. Azevedo, V. Lourenço, E. Soares, R. Thiago, R. Brandão, D. Civitarese, E.V. Brazil, M. Moreno, P. Valduriez, M. Mattoso, R. Cerqueira, and M.A.S. Netto Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2021. [J3][online] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Machine Learning (ML) has already fundamentally changed several businesses. More recently, it has also been profoundly impacting the computational science and engineering domains, like geoscience, climate science, and health science. In these domains, users need to perform comprehensive data analyses combining scientific data and ML models to provide for critical requirements, such as reproducibility, model explainability, and experiment data understanding. However, scientific ML is multidisciplinary, heterogeneous, and affected by the physical constraints of the domain, making such analyses even more challenging. In this work, we leverage workflow provenance techniques to build a holistic view to support the lifecycle of scientific ML. We contribute with (i) characterization of the lifecycle and taxonomy for data analyses; (ii) design principles to build this view, with a W3C PROV compliant data representation and a reference system architecture; and (iii) lessons learned after an evaluation in an Oil \& Gas case using an HPC cluster with 393 nodes and 946 GPUs. The experiments show that the principles enable queries that integrate domain semantics with ML models while keeping low overhead (<1\%), high scalability, and an order of magnitude of query acceleration under certain workloads against without our representation. [bibtex]@article{asouza2020workflow,
title={Workflow Provenance in the Lifecycle of Scientific Machine Learning},
author={Souza, Renan and G. Azevedo, Leonardo and Lourenço, Vítor and Soares, Elton and Thiago, Raphael and Brandão, Rafael and Civitarese, Daniel and Vital Brazil, Emilio and Moreno, Marcio and Valduriez, Patrick and Mattoso, Marta and Cerqueira, Renato and A. S. Netto, Marco},
year={2021},
abstract={Machine Learning (ML) has already fundamentally changed several businesses. More recently, it has also been profoundly impacting the computational science and engineering domains, like geoscience, climate science, and health science. In these domains, users need to perform comprehensive data analyses combining scientific data and ML models to provide for critical requirements, such as reproducibility, model explainability, and experiment data understanding. However, scientific ML is multidisciplinary, heterogeneous, and affected by the physical constraints of the domain, making such analyses even more challenging. In this work, we leverage workflow provenance techniques to build a holistic view to support the lifecycle of scientific ML.
We contribute with (i) characterization of the lifecycle and taxonomy for data analyses; (ii) design principles to build this view, with a W3C PROV compliant data representation and a reference system architecture; and (iii) lessons learned after an evaluation in an Oil \& Gas case using an HPC cluster with 393 nodes and 946 GPUs.
The experiments show that the principles enable queries that integrate domain semantics with ML models while keeping low overhead (<1\%), high scalability, and an order of magnitude of query acceleration under certain workloads against without our representation.},
url={https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.6544},
pdf={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.00330.pdf},
journal={Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience},
pages={1--21},
volume={e6544}
} |
| Adding Hyperknowledge-enabled data lineage to a machine learning workflow management system for oil and gas L.G. Azevedo, R. Souza, R. Brandão, V.N. Lourenço, M. Costalonga, M.d. Machado, M. Moreno, and R. Cerqueira First Break, 2020. [J4][doi] [bibtex]@article{azevedo2020adding,
title={Adding Hyperknowledge-enabled data lineage to a machine learning workflow management system for oil and gas},
author={Azevedo, Leonardo Guerreiro and Souza, Renan and Brandão, Rafael and Lourenço, Vítor N and Costalonga, Marcelo and de Machado, Marcelo and Moreno, Marcio and Cerqueira, Renato},
journal={First Break},
volume={38},
number={7},
pages={89--93},
year={2020},
publisher={European Association of Geoscientists \& Engineers},
doi = {10.3997/1365-2397.fb2020055}
} |
| Keeping Track of User Steering Actions in Dynamic Workflows R. Souza, V. Silva, J.J. Camata, A.L.G.A. Coutinho, P. Valduriez, and M. Mattoso Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019. [J5][doi] [online] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. In long-lasting scientific workflow executions in HPC machines, computational scientists (the users in this work) often need to fine-tune several workflow parameters. These tunings are done through user steering actions that may significantly improve performance (e.g., reduce execution time) or improve the overall results. However, in executions that last for weeks, users can lose track of what has been adapted if the tunings are not properly registered. In this work, we build on provenance data management to address the problem of tracking online parameter fine-tuning in dynamic workflows steered by users. We propose a lightweight solution to capture and manage provenance of the steering actions online with negligible overhead. The resulting provenance database relates tuning data with data for domain, dataflow provenance, execution, and performance, and is available for analysis at runtime. We show how users may get a detailed view of the execution, providing insights to determine when and how to tune. We discuss the applicability of our solution in different domains and validate its ability to allow for online capture and analyses of parameter fine-tunings in a real workflow in the Oil and Gas industry. In this experiment, the user could determine which tuned parameters influenced simulation accuracy and performance. The observed overhead for keeping track of user steering actions at runtime is less than 1\% of total execution time. [bibtex]@article{souza_keeping_2019,
title = {Keeping Track of User Steering Actions in Dynamic Workflows},
volume = {99},
issn = {0167-739X},
pdf = {https://hal-lirmm.ccsd.cnrs.fr/lirmm-02127456/document},
doi = {10.1016/j.future.2019.05.011},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.05.011},
pages = {624--643},
journal = {Future Generation Computer Systems},
author = {Souza, Renan and Silva, Vítor and Camata, Jose J. and Coutinho, Alvaro L. G. A. and Valduriez, Patrick and Mattoso, Marta},
year = {2019},
keyword = {Dynamic workflows, Computational steering, Provenance data, Parameter tuning},
abstract = {In long-lasting scientific workflow executions in HPC machines, computational scientists (the users in this work) often need to fine-tune several workflow parameters. These tunings are done through user steering actions that may significantly improve performance (e.g., reduce execution time) or improve the overall results. However, in executions that last for weeks, users can lose track of what has been adapted if the tunings are not properly registered. In this work, we build on provenance data management to address the problem of tracking online parameter fine-tuning in dynamic workflows steered by users. We propose a lightweight solution to capture and manage provenance of the steering actions online with negligible overhead. The resulting provenance database relates tuning data with data for domain, dataflow provenance, execution, and performance, and is available for analysis at runtime. We show how users may get a detailed view of the execution, providing insights to determine when and how to tune. We discuss the applicability of our solution in different domains and validate its ability to allow for online capture and analyses of parameter fine-tunings in a real workflow in the Oil and Gas industry. In this experiment, the user could determine which tuned parameters influenced simulation accuracy and performance. The observed overhead for keeping track of user steering actions at runtime is less than 1\% of total execution time.}
} |
| Adding Domain Data to Code Profiling Tools to Debug Workflow Parallel Execution V. Silva, L. Neves, R. Souza, A.L.G.A. Coutinho, D.d. Oliveira, and M. Mattoso Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018. [J6][doi] [bibtex]@article{silva_adding_2018,
title = {Adding Domain Data to Code Profiling Tools to Debug Workflow Parallel Execution},
issn = {0167-739X},
doi = {10.1016/j.future.2018.05.078},
author = {Silva, Vítor and Neves, Leonardo and Souza, Renan and Coutinho, Alvaro L. G. A. and de Oliveira, Daniel and Mattoso, Marta},
journal = {Future Generation Computer Systems},
year = {2018},
pages = {624--643},
keyword = {Scientific workflow, Debugging, Provenance, Performance analysis}
} |
| Data Reduction in Scientific Workflows Using Provenance Monitoring and User Steering R. Souza, V. Silva, A.L.G.A. Coutinho, P. Valduriez, and M. Mattoso Future Generation Computer Systems, 2017. [J7][doi] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Scientific workflows need to be iteratively, and often interactively, executed for large input datasets. Reducing data from input datasets is a powerful way to reduce overall execution time in such workflows. When this is accomplished online (i.e., without requiring the user to stop execution to reduce the data, and then resume), it can save much time. However, determining which subsets of the input data should be removed becomes a major problem. A related problem is to guarantee that the workflow system will maintain execution and data consistent with the reduction. Keeping track of how users interact with the workflow is essential for data provenance purposes. In this paper, we adopt the “human-in-the-loop” approach, which enables users to steer the running workflow and reduce subsets from datasets online. We propose an adaptive workflow monitoring approach that combines provenance data monitoring and computational steering to support users in analyzing the evolution of key parameters and determining the subset of data to remove. We extend a provenance data model to keep track of users’ interactions when they reduce data at runtime. In our experimental validation, we develop a test case from the oil and gas domain, using a 936-cores cluster. The results on this test case show that the approach yields reductions of 32\% of execution time and 14\% of the data processed. [bibtex]@article{Souza2017Data,
title = {Data Reduction in Scientific Workflows Using Provenance Monitoring and User Steering},
volume = {110},
pdf = {https://hal-lirmm.ccsd.cnrs.fr/lirmm-01679967/document},
issn = {0167-739X},
doi = {10.1016/j.future.2017.11.028},
author = {Souza, Renan and Silva, Vítor and Coutinho, Alvaro L. G. A. and Valduriez, Patrick and Mattoso, Marta},
journal = {Future Generation Computer Systems},
pages = {481--501},
keyword = {Scientific Workflows, Human in the Loop, Online Data Reduction, Provenance Data, Dynamic Workflows},
year = {2017},
abstract = {Scientific workflows need to be iteratively, and often interactively, executed for large input datasets. Reducing data from input datasets is a powerful way to reduce overall execution time in such workflows. When this is accomplished online (i.e., without requiring the user to stop execution to reduce the data, and then resume), it can save much time. However, determining which subsets of the input data should be removed becomes a major problem. A related problem is to guarantee that the workflow system will maintain execution and data consistent with the reduction. Keeping track of how users interact with the workflow is essential for data provenance purposes. In this paper, we adopt the “human-in-the-loop” approach, which enables users to steer the running workflow and reduce subsets from datasets online. We propose an adaptive workflow monitoring approach that combines provenance data monitoring and computational steering to support users in analyzing the evolution of key parameters and determining the subset of data to remove. We extend a provenance data model to keep track of users’ interactions when they reduce data at runtime. In our experimental validation, we develop a test case from the oil and gas domain, using a 936-cores cluster. The results on this test case show that the approach yields reductions of 32\% of execution time and 14\% of the data processed.}
} |
Conference and Workshop Papers 
| PROV-AGENT: Unified Provenance for Tracking AI Agent Interactions in Agentic Workflows R. Souza, A. Gueroudji, S. DeWitt, D. Rosendo, T. Ghosal, R. Ross, P. Balaprakash, and R.F.d. Silva 2025 IEEE International Conference on eScience (eScience), 2025. [C1][doi] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Large Language Models (LLMs) and other foundation models are increasingly used as the core of AI agents. In agentic workflows, these agents plan tasks, interact with humans and peers, and influence scientific outcomes across federated and heterogeneous environments. However, agents can hallucinate or reason incorrectly, propagating errors when one agent's output becomes another's input. Thus, assuring that agents' actions are transparent, traceable, reproducible, and reliable is critical to assess hallucination risks and mitigate their workflow impacts. While provenance techniques have long supported these principles, existing methods fail to capture and relate agent-centric metadata such as prompts, responses, and decisions with the broader workflow context and downstream outcomes. In this paper, we introduce PROV-AGENT, a provenance model that extends W3C PROV and leverages the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and data observability to integrate agent interactions into end-to-end workflow provenance. Our contributions include: (1) a provenance model tailored for agentic workflows, (2) a near real-time, open-source system for capturing agentic provenance, and (3) a cross-facility evaluation spanning edge, cloud, and HPC environments, demonstrating support for critical provenance queries and agent reliability analysis. [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_prov_agent_2025,
author = {Renan Souza and Amal Gueroudji and Stephen DeWitt and Daniel Rosendo and Tirthankar Ghosal and Robert Ross and Prasanna Balaprakash and Rafael Ferreira da Silva},
title = {PROV-AGENT: Unified Provenance for Tracking {AI} Agent Interactions in Agentic Workflows},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on e-Science},
year = {2025},
booktitle = { 2025 IEEE International Conference on eScience (eScience) },
doi = {10.1109/eScience65000.2025.00093},
location = {Chicago, U.S.A.},
pdf = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2508.02866},
publisher = {IEEE},
keywords = {Artificial Intelligence, Provenance, Machine Learning, AI workflows, ML workflows, Responsible AI, Trustworthy AI, Reproducibility, AI Lifecycle, Energy-efficient AI},
abstract = {Large Language Models (LLMs) and other foundation models are increasingly used as the core of AI agents. In agentic workflows, these agents plan tasks, interact with humans and peers, and influence scientific outcomes across federated and heterogeneous environments. However, agents can hallucinate or reason incorrectly, propagating errors when one agent's output becomes another's input. Thus, assuring that agents' actions are transparent, traceable, reproducible, and reliable is critical to assess hallucination risks and mitigate their workflow impacts. While provenance techniques have long supported these principles, existing methods fail to capture and relate agent-centric metadata such as prompts, responses, and decisions with the broader workflow context and downstream outcomes. In this paper, we introduce PROV-AGENT, a provenance model that extends W3C PROV and leverages the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and data observability to integrate agent interactions into end-to-end workflow provenance. Our contributions include: (1) a provenance model tailored for agentic workflows, (2) a near real-time, open-source system for capturing agentic provenance, and (3) a cross-facility evaluation spanning edge, cloud, and HPC environments, demonstrating support for critical provenance queries and agent reliability analysis.}
} |
| LLM Agents for Interactive Workflow Provenance: Reference Architecture and Evaluation Methodology R. Souza, T. Poteet, B. Etz, D. Rosendo, A. Gueroudji, W. Shin, P. Balaprakash, and R.F.d. Silva Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science (WORKS) co-located with the ACM/IEEE International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC), 2025. [C2][doi] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Modern scientific discovery increasingly relies on workflows that process data across the Edge, Cloud, and High Performance Computing (HPC) continuum. Comprehensive and in-depth analyses of these data are critical for hypothesis validation, anomaly detection, reproducibility, and impactful findings. Although workflow provenance techniques support such analyses, at large scale, the provenance data become complex and difficult to analyze. Existing systems depend on custom scripts, structured queries, or static dashboards, limiting data interaction. In this work, we introduce an evaluation methodology, reference architecture, and open-source implementation that leverages interactive Large Language Model (LLM) agents for runtime data analysis. Our approach uses a lightweight, metadata-driven design that translates natural language into structured provenance queries. Evaluations across LLaMA, GPT, Gemini, and Claude, covering diverse query classes and a real-world chemistry workflow, show that modular design, prompt tuning, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enable accurate and insightful LLM agent responses beyond recorded provenance. [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_llm_agents_works_sc25,
title = {{LLM} Agents for Interactive Workflow Provenance: Reference Architecture and Evaluation Methodology},
author={Souza, Renan and Poteet, Timothy and Etz, Brian and Rosendo, Daniel and Gueroudji, Amal and Shin, Woong and Balaprakash, Prasanna and Ferreira da Silva, Rafael},
booktitle = {Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science ({WORKS}) co-located with the {ACM}/{IEEE} International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis ({SC})},
year = {2025},
address = {St Louis, MO, USA},
pdf = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.13978},
publisher = {ACM},
abstract = {Modern scientific discovery increasingly relies on workflows that process data across the Edge, Cloud, and High Performance Computing (HPC) continuum. Comprehensive and in-depth analyses of these data are critical for hypothesis validation, anomaly detection, reproducibility, and impactful findings. Although workflow provenance techniques support such analyses, at large scale, the provenance data become complex and difficult to analyze. Existing systems depend on custom scripts, structured queries, or static dashboards, limiting data interaction. In this work, we introduce an evaluation methodology, reference architecture, and open-source implementation that leverages interactive Large Language Model (LLM) agents for runtime data analysis. Our approach uses a lightweight, metadata-driven design that translates natural language into structured provenance queries. Evaluations across LLaMA, GPT, Gemini, and Claude, covering diverse query classes and a real-world chemistry workflow, show that modular design, prompt tuning, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enable accurate and insightful LLM agent responses beyond recorded provenance.},
doi = {10.1145/3731599.3767582},
keywords = {scientific workflows, provenance, LLM agents, Large language models, AI agents, agentic workflows, agentic provenance}
} |
| The (R) evolution of Scientific Workflows in the Agentic AI Era: Towards Autonomous Science W. Shin, R. Souza, D. Rosendo, F. Suter, F. Wang, P. Balaprakash, and R.F.d. Silva Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science (WORKS) co-located with the ACM/IEEE International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC), 2025. [C3][pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{shin2025r,
title={The (R) evolution of Scientific Workflows in the Agentic AI Era: Towards Autonomous Science},
author={Shin, Woong and Souza, Renan and Rosendo, Daniel and Suter, Fr{\'e}d{\'e}ric and Wang, Feiyi and Balaprakash, Prasanna and da Silva, Rafael Ferreira},
booktitle = {Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science ({WORKS}) co-located with the {ACM}/{IEEE} International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis ({SC})},
year = {2025},
address = {St Louis, MO, USA},
pdf = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.09915},
publisher = {ACM},
keywords = {Agentic AI, Agentic Workflows, Autonomous Science, Scientific AI Systems, Swarm Intelligence}
} |
| AI Agents for Enabling Autonomous Experiments at ORNL’s HPC and Manufacturing User Facilities D. Rosendo, S. DeWitt, R. Souza, P. Austria, T. Ghosal, M. McDonnell, R. Miller, T.J. Skluzacek, J. Haley, B. Turcksin, and others Extreme-Scale Experiment-in-the-Loop Computing (XLOOP) co-located with the ACM/IEEE International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC), 2025. [C4][doi] [pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{rosendo2025ai,
title={AI Agents for Enabling Autonomous Experiments at ORNL’s HPC and Manufacturing User Facilities},
author={Rosendo, Daniel and DeWitt, Stephen and Souza, Renan and Austria, Phillipe and Ghosal, Tirthankar and McDonnell, Marshall and Miller, Ross and Skluzacek, Tyler J and Haley, James and Turcksin, Bruno and others},
booktitle = {Extreme-Scale Experiment-in-the-Loop Computing ({XLOOP}) co-located with the {ACM}/{IEEE} International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis ({SC})},
year = {2025},
address = {St Louis, MO, USA},
doi = {10.1145/3731599.3767592},
pdf = {https://rafaelsilva.com/files/publications/rosendo2025xloop.pdf},
publisher = {ACM},
} |
| ControlA: Agentic Workflow Control Mechanisms for Reliable Science A. Gueroudji, T. Mallick, R. Souza, R.F.d. Silva, R. Ross, M. Dorier, P. Carns, K. Chard, and I. Foster IEEE International Conference on e-Science, 2025. [C5] [bibtex]@inproceedings{amal_2025,
author = {Amal Gueroudji and Tanwi Mallick and Renan Souza and Rafael Ferreira da Silva and
Robert Ross and Matthieu Dorier and Philip Carns and Kyle Chard and Ian Foster},
title = {ControlA: Agentic Workflow Control Mechanisms for Reliable Science},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on e-Science},
year = {2025},
location = {Chicago, USA},
publisher = {IEEE},
keywords = {Agentic AI, Agentic workflows, Reliability, Safety, Agentic Systems}
} |
| Workflow Provenance in the Computing Continuum for Responsible, Trustworthy, and Energy-Efficient AI R. Souza, S. Caino-Lores, M. Coletti, T.J. Skluzacek, A. Costan, F. Suter, M. Mattoso, and R.F.d. Silva IEEE International Conference on e-Science, 2024. [C6][doi] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. As Artificial Intelligence (AI) becomes more pervasive in our society, it is crucial to develop, deploy, and assess Responsible and Trustworthy AI (RTAI) models, i.e., those that consider not only accuracy but also other aspects, such as explainability, fairness, and energy efficiency. Workflow provenance data have historically enabled critical capabilities towards RTAI. Provenance data derivation paths contribute to responsible workflows through transparency in tracking artifacts and resource consumption. Provenance data are well-known for their trustworthiness, helping explainability, reproducibility, and accountability. However, there are complex challenges to achieving RTAI, which are further complicated by the heterogeneous infrastructure in the computing continuum (Edge-Cloud-HPC) used to develop and deploy models. As a result, a significant research and development gap remains between workflow provenance data management and RTAI. In this paper, we present a vision of the pivotal role of workflow provenance in supporting RTAI and discuss related challenges. We present a schematic view of the relationship between RTAI and provenance, and highlight open research directions. [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_rtai_2024,
author = {Renan Souza and Silvina Caino-Lores and Mark Coletti and Tyler J. Skluzacek and Alexandru Costan and Frederic Suter and Marta Mattoso and Rafael Ferreira da Silva},
title = {Workflow Provenance in the Computing Continuum for Responsible, Trustworthy, and Energy-Efficient {AI}},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on e-Science},
year = {2024},
location = {Osaka, Japan},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1109/e-Science62913.2024.10678731},
pdf = {https://hal.science/hal-04902079v1/document},
publisher = {IEEE},
keywords = {Artificial Intelligence, Provenance, Machine Learning, AI workflows, ML workflows, Responsible AI, Trustworthy AI, Reproducibility, AI Lifecycle, Energy-efficient AI},
abstract = {As Artificial Intelligence (AI) becomes more pervasive in our society, it is crucial to develop, deploy, and assess Responsible and Trustworthy AI (RTAI) models, i.e., those that consider not only accuracy but also other aspects, such as explainability, fairness, and energy efficiency. Workflow provenance data have historically enabled critical capabilities towards RTAI. Provenance data derivation paths contribute to responsible workflows through transparency in tracking artifacts and resource consumption. Provenance data are well-known for their trustworthiness, helping explainability, reproducibility, and accountability. However, there are complex challenges to achieving RTAI, which are further complicated by the heterogeneous infrastructure in the computing continuum (Edge-Cloud-HPC) used to develop and deploy models. As a result, a significant research and development gap remains between workflow provenance data management and RTAI. In this paper, we present a vision of the pivotal role of workflow provenance in supporting RTAI and discuss related challenges. We present a schematic view of the relationship between RTAI and provenance, and highlight open research directions.}
} |
| Towards Cross-Facility Workflows Orchestration through Distributed Automation T.J. Skluzacek, R. Souza, M. Coletti, F. Suter, and R.F.d. Silva Practice and Experience in Advanced Research Computing (PEARC 24), 2024. [C7][doi] [online] [bibtex]@inproceedings{skluzacek_pearc_2024,
author = {Tyler J. Skluzacek and Renan Souza and Mark Coletti and Frederic Suter and Rafael Ferreira da Silva},
title = {Towards Cross-Facility Workflows Orchestration through Distributed Automation},
booktitle = {Practice and Experience in Advanced Research Computing (PEARC 24)},
year = {2024},
location = {Providence, RI, USA},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3626203.3670606},
doi = {10.1145/3626203.3670606},
} |
| Eco-Driven AI-HPC: Optimizing Energy Efficiency in Distributed Scientific Workflows R.F.d. Silva, W. Shin, F. Suter, A. Gainaru, R. Souza, D. Dietz, and S. Jha Energy-Efficient Computing for Science Workshop, 2024. [C8] [bibtex]@inproceedings{silva_ee_2024,
author = {Rafael Ferreira da Silva and Woong Shin and Frederic Suter and Ana Gainaru and Renan Souza and Dan Dietz and Shantenu Jha},
title = {{Eco-Driven AI-HPC}: Optimizing Energy Efficiency in Distributed Scientific Workflows},
booktitle = {Energy-Efficient Computing for Science Workshop},
year = {2024},
location = {Bethesda, MD, USA}
} |
| Advancing Computational Earth Sciences: Innovations and Challenges in Scientific HPC Workflows R.F.d. Silva, K. Maheshwari, T. Skluzacek, R. Souza, and S. Wilkinson European Geosciences Union (EGU), 2024. [C9] [bibtex]@inproceedings{dasilva_agu_2024,
title={Advancing Computational Earth Sciences: Innovations and Challenges in Scientific HPC Workflows},
author={da Silva, Rafael Ferreira and Maheshwari, Ketan and Skluzacek, T and Souza, Renan and Wilkinson, Sean},
booktitle={European Geosciences Union (EGU)},
year={2024},
} |
| Integrating Evolutionary Algorithms with Distributed Deep Learning for Optimizing Hyperparameters on HPC System M. Coletti, R. Souza, T.J. Skluzacek, F. Suter, and R.F.d. Silva Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science (WORKS) workshop co-located with the ACM/IEEE International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC), 2024. [C10] [bibtex]@inproceedings{coletti_2024,
author = {Mark Coletti and Renan Souza and Tyler J. Skluzacek and Frederic Suter and Rafael Ferreira da Silva},
title = {Integrating Evolutionary Algorithms with Distributed Deep Learning for Optimizing Hyperparameters on {HPC} System},
booktitle = {Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science ({WORKS}) workshop co-located with the {ACM}/{IEEE} International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis ({SC})},
year = {2024},
location = {Atlanta, USA},
publisher = {IEEE}
} |
| HKPoly: A Polystore Architecture to Support Data Linkage and Queries on Distributed and Heterogeneous Data L.G. Azevedo, R. Souza, E. Soares, R.M. Thiago, J.C.C. Tesolin, A.C.C.M. Oliveira, and M.F. Moreno Proceedings of the 20th Brazilian Symposium on Information Systems (SBSI), 2024. [C11][doi] [online] [bibtex]@inproceedings{azevedo_hkpoly2024,
author = {Azevedo, Leonardo Guerreiro and Souza, Renan and Soares, Elton and Thiago, Raphael Melo and Tesolin, Julio Cesar Cardoso and Oliveira, Anna Carolina Carvalho Moreira and Moreno, Marcio Ferreira},
title = {{HKPoly}: A Polystore Architecture to Support Data Linkage and Queries on Distributed and Heterogeneous Data},
year = {2024},
isbn = {9798400709968},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3658271.3658322},
doi = {10.1145/3658271.3658322},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 20th Brazilian Symposium on Information Systems (SBSI)},
articleno = {50},
numpages = {10},
keywords = {Business process, Database integration, Distributed databases, Microservices, Provenance., Query processing},
series = {SBSI '24}
} |
| Towards Lightweight Data Integration using Multi-workflow Provenance and Data Observability R. Souza, T.J. Skluzacek, S.R. Wilkinson, M. Ziatdinov, and R.F.d. Silva IEEE International Conference on e-Science, 2023. [C12][doi] [online] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Modern large-scale scientific discovery requires multidisciplinary collaboration across diverse computing facilities, including High Performance Computing (HPC) machines and the Edge-to-Cloud continuum. Integrated data analysis plays a crucial role in scientific discovery, especially in the current AI era, by enabling Responsible AI development, FAIR, Reproducibility, and User Steering. However, the heterogeneous nature of science poses challenges such as dealing with multiple supporting tools, cross-facility environments, and efficient HPC execution. Building on data observability, adapter system design, and provenance, we propose MIDA: an approach for lightweight runtime Multi-workflow Integrated Data Analysis. MIDA defines data observability strategies and adaptability methods for various parallel systems and machine learning tools. With observability, it intercepts the dataflows in the background without requiring instrumentation while integrating domain, provenance, and telemetry data at runtime into a unified database ready for user steering queries. We conduct experiments showing end-to-end multi-workflow analysis integrating data from Dask and MLFlow in a real distributed deep learning use case for materials science that runs on multiple environments with up to 276 GPUs in parallel. We show near-zero overhead running up to 100,000 tasks on 1,680 CPU cores on the Summit supercomputer. [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza2023towards,
title={Towards Lightweight Data Integration using Multi-workflow Provenance and Data Observability},
author={Souza, Renan and Skluzacek, Tyler J and Wilkinson, Sean R and Ziatdinov, Maxim and da Silva, Rafael Ferreira},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on e-Science},
doi={10.1109/e-Science58273.2023.10254822},
url={https://doi.org/10.1109/e-Science58273.2023.10254822},
pdf={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2308.09004.pdf},
year={2023},
abstract={Modern large-scale scientific discovery requires multidisciplinary collaboration across diverse computing facilities, including High Performance Computing (HPC) machines and the Edge-to-Cloud continuum. Integrated data analysis plays a crucial role in scientific discovery, especially in the current AI era, by enabling Responsible AI development, FAIR, Reproducibility, and User Steering. However, the heterogeneous nature of science poses challenges such as dealing with multiple supporting tools, cross-facility environments, and efficient HPC execution. Building on data observability, adapter system design, and provenance, we propose MIDA: an approach for lightweight runtime Multi-workflow Integrated Data Analysis. MIDA defines data observability strategies and adaptability methods for various parallel systems and machine learning tools. With observability, it intercepts the dataflows in the background without requiring instrumentation while integrating domain, provenance, and telemetry data at runtime into a unified database ready for user steering queries. We conduct experiments showing end-to-end multi-workflow analysis integrating data from Dask and MLFlow in a real distributed deep learning use case for materials science that runs on multiple environments with up to 276 GPUs in parallel. We show near-zero overhead running up to 100,000 tasks on 1,680 CPU cores on the Summit supercomputer.}
} |
| ProvLight: Efficient Workflow Provenance Capture on the Edge-to-Cloud Continuum D. Rosendo, M. Mattoso, A. Costan, R. Souza, D. Pina, P. Valduriez, and G. Antoniu IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing, 2023. [C13][doi] [online] [pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{rosendo2023provlight,
title={{ProvLight}: Efficient Workflow Provenance Capture on the Edge-to-Cloud Continuum},
author={Rosendo, Daniel and Mattoso, Marta and Costan, Alexandru and Souza, Renan and Pina, D{\'e}bora and Valduriez, Patrick and Antoniu, Gabriel},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing},
doi={10.1109/CLUSTER52292.2023.00026},
url={https://www.computer.org/csdl/proceedings-article/cluster/2023/079200a221/1SfUrCnjgAM},
pdf={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.10658},
year={2023}
} |
| User Steering Support in Large-scale Workflows R. Souza PhD Thesis Contest: Brazilian Symposium on Databases (SBBD), 2021. [C14][pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_2021_ctd_sbbd,
title={User Steering Support in Large-scale Workflows},
author={Souza, Renan},
booktitle = {PhD Thesis Contest: Brazilian Symposium on Databases ({SBBD})},
year={2021},
pdf = {https://sol.sbc.org.br/index.php/sbbd_estendido/article/download/18185/18019}
} |
| A Recommender for Choosing Data Systems based on Application Profiling and Benchmarking E. Soares, R. Souza, R. Thiago, M. Machado, and L. Azevedo Brazilian Symposium on Databases (SBBD), 2021. [C15][pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{soares_2021_recommender,
title={A Recommender for Choosing Data Systems based on Application Profiling and Benchmarking},
author={Soares, Elton and Souza, Renan and Thiago, Raphael and Machado, Marcelo and Azevedo, Leonardo},
booktitle={Brazilian Symposium on Databases ({SBBD})},
year={2021},
pages = {265-270},
pdf = {https://sol.sbc.org.br/index.php/sbbd/article/download/17883/17717/}
} |
| Context-aware Execution Migration Tool for Data Science Jupyter Notebooks on Hybrid Clouds R.L. Cunha, L.V. Real, R. Souza, B. Silva, and M.A. Netto IEEE International Conference on e-Science, 2021. [C16][doi] [pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{cunha_2021_context,
title={Context-aware Execution Migration Tool for Data Science Jupyter Notebooks on Hybrid Clouds},
author={Cunha, Renato LF and Real, Lucas V and Souza, Renan and Silva, Bruno and Netto, Marco AS},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on e-Science},
year={2021},
doi={10.1109/eScience51609.2021.00013},
pdf={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.00187.pdf}
} |
| Supporting Polystore Queries using Provenance in a Hyperknowledge Graph L. Azevedo, R. Souza, E. Soares, R. Thiago, A. Oliveira, and M. Moreno International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC), 2021. [C17][pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{azevedo_supporting_2021,
title={Supporting Polystore Queries using Provenance in a Hyperknowledge Graph},
author={Azevedo, Leonardo and Souza, Renan and Soares, Elton and Thiago, Raphael and Oliveira, Anna and Moreno, Marcio},
booktitle={International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC)},
year={2021},
pages = {1--4},
pdf = {http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2980/paper368.pdf}
} |
| Runtime Steering of Parallel CFD Simulations R. Souza, J. Camata, M. Mattoso, and A. Coutinho International Conference on Parallel Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2020. [C18] [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_runtime_2020,
title = {Runtime Steering of Parallel CFD Simulations},
booktitle = {International Conference on Parallel Computational Fluid Dynamics},
author = {Souza, Renan and Camata, J. and Mattoso, Marta and Coutinho, Alvaro},
year = {2020}
} |
| Managing Data Lineage of O\&G Machine Learning Models: The Sweet Spot for Shale Use Case R. Thiago, R. Souza, L. Azevedo, E. Soares, R. Santos, W. Santos, M.D. Bayser, M. Cardoso, M. Moreno, and R. Cerqueira European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers (EAGE) Digitalization Conference and Exhibition, 2020. [C19][doi] [pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_eage_2020,
title = {Managing Data Lineage of {O\&G} Machine Learning Models: The Sweet Spot for Shale Use Case},
booktitle = {European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers (EAGE) Digitalization Conference and Exhibition},
author = {Thiago, Raphael and Souza, Renan and Azevedo, L. and Soares, E. and Santos, Rodrigo, and Santos, Wallas and De Bayser, Max and Cardoso, M. and Moreno, M. and Cerqueira, Renato},
year = {2020},
doi = {10.3997/2214-4609.202032075},
pdf = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2003.04915.pdf}
} |
| Supporting the Training of Physics Informed Neural Networks for Seismic Inversion Using Provenance R. Souza, A. Codas, J.A.N. Junior, M.P. Quinones, L. Azevedo, R. Thiago, E. Soares, M. Cardoso, and L. Martins American Association of Petroleum Geologists Annual Convention and Exhibition (AAPG), 2020. [C20] [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_aapg_2020,
title = {Supporting the Training of Physics Informed Neural Networks for Seismic Inversion Using Provenance},
booktitle = {American Association of Petroleum Geologists Annual Convention and Exhibition ({AAPG})},
author = {Souza, Renan and Codas, A. and Nogueira Junior, J. Almeida and Quinones, M. P. and Azevedo, L. and Thiago, R. and Soares, E. and Cardoso, M. and Martins, L.},
year = {2020}
} |
| A Knowledge-Based Approach for Structuring Cyclic Workflows R. Brandão, V. Lourenço, M. Machado, L. Azevedo, M. Cardoso, R. Souza, G. Lima, R. Cerqueira, and M. Moreno International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC), 2020. [C21] [bibtex]@inproceedings{brandao2020knowledge,
title={A Knowledge-Based Approach for Structuring Cyclic Workflows},
author={Brand{\~a}o, Rafael and Louren{\c{c}}o, Vitor and Machado, Marcelo and Azevedo, Leonardo and Cardoso, Marcelo and Souza, Renan and Lima, Guilherme and Cerqueira, Renato and Moreno, Marcio},
booktitle={International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC)},
year={2020}
} |
| Cycle Orchestrator: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Structuring Cyclic ML Pipelines in the O\&G Industry R. Brandão, V. Lourenço, M. Machado, L. Azevedo, M. Cardoso, R. Souza, G. Lima, R. Cerqueira, and M. Moreno International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC), 2020. [C22] [bibtex]@inproceedings{brandao2020cycle,
title={Cycle Orchestrator: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Structuring Cyclic ML Pipelines in the O\&G Industry},
author={Brand{\~a}o, Rafael and Louren{\c{c}}o, Vitor and Machado, Marcelo and Azevedo, Leonardo and Cardoso, Marcelo and Souza, Renan and Lima, Guilherme and Cerqueira, Renato and Moreno, Marcio},
booktitle={International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC)},
year={2020}
} |
| Modern Federated Databases: an Overview L. Azevedo, R. Souza, E. Soares, and M. Moreno International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS), 2020. [C23] [bibtex]@inproceedings{azevedo_federated_2020,
title = {Modern Federated Databases: an Overview},
booktitle = {International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS)},
author = {Azevedo, Leonardo and Souza, Renan and Soares, Elton and Moreno, Marcio},
year = {2020}
} |
| Experiencing ProvLake to Manage the Data Lineage of AI Workflows L. Azevedo, R. Souza, R. Thiago, E. Soares, and M. Moreno Innovation Summit on Information Systems (EISI) in Brazilian Symposium in Information Systems (SBSI), 2020. [C24] [bibtex]@inproceedings{azevedo_experiencing_2020,
title = {Experiencing {ProvLake} to Manage the Data Lineage of AI Workflows},
booktitle = {Innovation Summit on Information Systems (EISI) in Brazilian Symposium in Information Systems (SBSI)},
author = {Azevedo, Leonardo and Souza, Renan and Thiago, Raphael and Soares, Elton and Moreno, Marcio},
year = {2020}
} |
| Provenance Data in the Machine Learning Lifecycle in Computational Science and Engineering R. Souza, L. Azevedo, V. Lourenço, E. Soares, R. Thiago, R. Brandão, D. Civitarese, E.V. Brazil, M. Moreno, P. Valduriez, M. Mattoso, R. Cerqueira, and M.A.S. Netto Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science (WORKS) co-located with the ACM/IEEE International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC), 2019. [C25][doi] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Machine Learning (ML) has become essential in several industries. In Computational Science and Engineering (CSE), the complexity of the ML lifecycle comes from the large variety of data, scientists' expertise, tools, and workflows. If data are not tracked properly during the lifecycle, it becomes unfeasible to recreate a ML model from scratch or to explain to stakeholders how it was created. The main limitation of provenance tracking solutions is that they cannot cope with provenance capture and integration of domain and ML data processed in the multiple workflows in the lifecycle while keeping the provenance capture overhead low. To handle this problem, in this paper we contribute with a detailed characterization of provenance data in the ML lifecycle in CSE; a new provenance data representation, called PROV-ML, built on top of W3C PROV and ML Schema; and extensions to a system that tracks provenance from multiple workflows to address the characteristics of ML and CSE, and to allow for provenance queries with a standard vocabulary. We show a practical use in a real case in the Oil and Gas industry, along with its evaluation using 48 GPUs in parallel. [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_provenancedata_2019,
title={Provenance Data in the Machine Learning Lifecycle in Computational Science and Engineering},
author={Souza, Renan and Azevedo, Leonardo and Lourenço, Vítor and Soares, Elton and Thiago, Raphael and Brandão, Rafael and Civitarese, Daniel and Vital Brazil, Emilio and Moreno, Marcio and Valduriez, Patrick and Mattoso, Marta and Cerqueira, Renato and A. S. Netto, Marco},
year={2019},
pages = {1--10},
booktitle = {Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science ({WORKS}) co-located with the {ACM}/{IEEE} International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis ({SC})},
pdf = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.04223},
doi = {10.1109/WORKS49585.2019.00006},
keywords = {Machine Learning Lifecycle, Workflow Provenance, Computational Science and Engineering},
abstract = {Machine Learning (ML) has become essential in several industries. In Computational Science and Engineering (CSE), the complexity of the ML lifecycle comes from the large variety of data, scientists' expertise, tools, and workflows. If data are not tracked properly during the lifecycle, it becomes unfeasible to recreate a ML model from scratch or to explain to stakeholders how it was created. The main limitation of provenance tracking solutions is that they cannot cope with provenance capture and integration of domain and ML data processed in the multiple workflows in the lifecycle while keeping the provenance capture overhead low. To handle this problem, in this paper we contribute with a detailed characterization of provenance data in the ML lifecycle in CSE; a new provenance data representation, called PROV-ML, built on top of W3C PROV and ML Schema; and extensions to a system that tracks provenance from multiple workflows to address the characteristics of ML and CSE, and to allow for provenance queries with a standard vocabulary. We show a practical use in a real case in the Oil and Gas industry, along with its evaluation using 48 GPUs in parallel.}
} |
| Managing Data Traceability in the Data Lifecycle for Deep Learning Applied to Seismic Data R. Souza, E.V. Brazil, L. Azevedo, R. Ferreira, D. Chevitarese, E. Soares, R. Thiago, M. Nery, V. Torres, and R. Cerqueira American Association of Petroleum Geologists Annual Convention and Exhibition (AAPG), 2019. [C26][online] [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_managing_2019,
title = {Managing Data Traceability in the Data Lifecycle for Deep Learning Applied to Seismic Data},
url = {https://www.searchanddiscovery.com/abstracts/html/2019/ace2019/abstracts/1718.html},
booktitle = {American Association of Petroleum Geologists Annual Convention and Exhibition ({AAPG})},
author = {Souza, Renan and Brazil, Emilio Vital and Azevedo, Leonardo and Ferreira, Rodrigo and Chevitarese, Daniel and Soares, Elton and Thiago, Raphael and Nery, Marcelo and Torres, Viviane and Cerqueira, Renato},
year = {2019}
} |
| Efficient Runtime Capture of Multiworkflow Data Using Provenance R. Souza, L. Azevedo, R. Thiago, E. Soares, M. Nery, M. Netto, E.V. Brazil, R. Cerqueira, P. Valduriez, and M. Mattoso IEEE International Conference on e-Science, 2019. [C27][doi] [online] [pdf] [abstract]Abstract. Computational Science and Engineering (CSE) projects are typically developed by multidisciplinary teams. Despite being part of the same project, each team manages its own workflows, using specific execution environments and data processingtools. Analyzing the data processed by all workflows globally is a core task in a CSE project. However, this analysis is hard because the data generated by these workflows are not integrated. In addition, since these workflows may take a long time to execute, data analysis needs to be done at runtime to reduce cost and time of the CSE project. A typical solution in scientific data analysis is to capture and relate the data in a provenance database while the workflows run, thus allowing for data analysisat runtime. However, the main problem is that such data capture competes with the running workflows, adding significant overhead to their execution. To mitigate this problem, we introduce in this paper a system called ProvLake, which adopts design principles for providing efficientdistributed data capture from the workflows. While capturing the data, ProvLake logically integrates and ingests them into a provenance database ready for analyses at runtime. We validated ProvLake ina real use case in the O&G industry encompassing four workflows that process 5TB datasets for a deep learning classifier. Compared with Komadu, the closest solution that meets our goals, our approach enables runtime multiworkflow data analysis with much smaller overhead, such as 0.1\%. [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_efficient_2019,
title = {Efficient Runtime Capture of Multiworkflow Data Using Provenance},
pdf = {https://hal-lirmm.ccsd.cnrs.fr/lirmm-02265932/document},
pages = {1--10},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on e-Science},
author = {Souza, Renan and Azevedo, Leonardo and Thiago, Raphael and Soares, Elton and Nery, Marcelo and Netto, Marco and Brazil, Emilio Vital and Cerqueira, Renato and Valduriez, Patrick and Mattoso, Marta},
year = {2019},
pdf = {https://hal-lirmm.ccsd.cnrs.fr/lirmm-02265932/document},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1109/eScience.2019.00047},
keywords = {Multiworkflow provenance, Multi-Data Lineage, Data Lake Provenance, ProvLake},
doi = {10.1109/eScience.2019.00047},
abstract = {Computational Science and Engineering (CSE) projects are typically developed by multidisciplinary teams. Despite being part of the same project, each team manages its own workflows, using specific execution environments and data processingtools. Analyzing the data processed by all workflows globally is a core task in a CSE project. However, this analysis is hard because the data generated by these workflows are not integrated. In addition, since these workflows may take a long time to execute, data analysis needs to be done at runtime to reduce cost and time of the CSE project. A typical solution in scientific data analysis is to capture and relate the data in a provenance database while the workflows run, thus allowing for data analysisat runtime. However, the main problem is that such data capture competes with the running workflows, adding significant overhead to their execution. To mitigate this problem, we introduce in this paper a system called ProvLake, which adopts design principles for providing efficientdistributed data capture from the workflows. While capturing the data, ProvLake logically integrates and ingests them into a provenance database ready for analyses at runtime. We validated ProvLake ina real use case in the O&G industry encompassing four workflows that process 5TB datasets for a deep learning classifier. Compared with Komadu, the closest solution that meets our goals, our approach enables runtime multiworkflow data analysis with much smaller overhead, such as 0.1\%.}
} |
| Scientific Data Analysis Using Data-Intensive Scalable Computing: the SciDISC Project P. Valduriez, M. Mattoso, R. Akbarinia, H. Borges, J. Camata, A.L.G.A. Coutinho, D. Gaspar, N. Lemus, J. Liu, H. Lustosa, F. Masseglia, F.N.D. Silva, V. Silva, R. Souza, K. Ocaña, E. Ogasawara, D. Oliveira, E. Pacitti, F. Porto, and D. Shasha LADaS: Latin America Data Science Workshop, 2018. [C28][online] [pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{valduriez:lirmm-01867804,
title = {{Scientific Data Analysis Using Data-Intensive Scalable Computing: the SciDISC Project}},
author = {Valduriez, Patrick and Mattoso, Marta and Akbarinia, Reza and Borges, Heraldo and Camata, José and Coutinho, Alvaro L G A and Gaspar, Daniel and Lemus, Noel and Liu, Ji and Lustosa, Hermano and Masseglia, Florent and Nogueira Da Silva, Fabricio and Silva, Vitor and Souza, Renan and Ocaña, Kary and Ogasawara, Eduardo and Oliveira, Daniel and Pacitti, Esther and Porto, F{\'a}bio and Shasha, Dennis},
url = {https://hal-lirmm.ccsd.cnrs.fr/lirmm-01867804},
booktitle = {{LADaS: Latin America Data Science Workshop}},
address = {Rio de Janeiro, Brazil},
publisher = {{CEUR-WS.org}},
volume = {CEUR Workshop Proceedings},
number = {2170},
year = {2018},
keywords = {HPC ; Scalable Data-Intensive Computing ; Big data ; Scientific data},
pdf = {https://hal-lirmm.ccsd.cnrs.fr/lirmm-01867804/file/ldas%202018%20-%20scidisc.pdf}
} |
| Towards a human-in-the-loop library for tracking hyperparameter tuning in deep learning development R. Souza, L. Neves, L. Azeredo, R. Luiz, E. Tady, P. Cavalin, and M. Mattoso Latin American Data Science (LaDaS) workshop co-located with the Very Large Database (VLDB) conference, 2018. [C29][pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_towards_2018,
location = {Rio de Janeiro, Brazil},
title = {Towards a human-in-the-loop library for tracking hyperparameter tuning in deep learning development},
pdf = {http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2170/paper12.pdf},
eventtitle = {Latin American Data Science ({LaDaS}) workshop co-located with the Very Large Database ({VLDB}) conference},
pages = {84--87},
booktitle = {Latin American Data Science ({LaDaS}) workshop co-located with the Very Large Database ({VLDB}) conference},
author = {Souza, Renan and Neves, Liliane and Azeredo, Leonardo and Luiz, Ricardo and Tady, Elaine and Cavalin, Paulo and Mattoso, Marta},
year = {2018}
} |
| Ravel: A MAS orchestration platform for Human-Chatbots Conversations M.G.d. Bayser, C. Pinhanez, H. Candello, M. Affonso, M.P. Vasconcelos, M.A. Guerra, P. Cavalin, and R. Souza International Workshop on Engineering Multi-Agent Systems (EMAS@AAMAS 2018), 2018. [C30][pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{de2018ravel,
title={Ravel: A MAS orchestration platform for Human-Chatbots Conversations},
author={de Bayser, Maira Gatti and Pinhanez, Claudio and Candello, Heloisa and Affonso, Marisa and Vasconcelos, Mauro Pichiliani and Guerra, Melina Alberio and Cavalin, Paulo and Souza, Renan},
booktitle={International Workshop on Engineering Multi-Agent Systems (EMAS@AAMAS 2018)},
pdf = {http://emas2018.dibris.unige.it/images/papers/EMAS18-19.pdf},
year={2018}
} |
| Provenance of Dynamic Adaptations in User-Steered Dataflows R. Souza and M. Mattoso Provenance and Annotation of Data and Processes - International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), 2018. [C31][doi] [pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{Souza2018Provenance,
title = {Provenance of Dynamic Adaptations in User-Steered Dataflows},
author = {Souza, Renan and Mattoso, Marta},
isbn = {978-3-319-98379-0},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-319-98379-0_2},
series = {Lecture Notes in Computer Science ({LNCS})},
pages = {16--29},
publisher = {Springer International Publishing},
year = {2018},
booktitle = {Provenance and Annotation of Data and Processes - International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW)},
pdf = {https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327460259_Provenance_of_Dynamic_Adaptations_in_User-Steered_Dataflows_7th_International_Provenance_and_Annotation_Workshop_IPAW_2018_London_UK_July_9-10_2018_Proceedings}
} |
| Capturing Provenance for Runtime Data Analysis in Computational Science and Engineering Applications V. Silva, R. Souza, J. Camata, D.d. Oliveira, P. Valduriez, A.L.G.A. Coutinho, and M. Mattoso Provenance and Annotation of Data and Processes - International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW), 2018. [C32][doi] [bibtex]@inproceedings{Silva2018Capturing,
title = {Capturing Provenance for Runtime Data Analysis in Computational Science and Engineering Applications},
isbn = {978-3-319-98379-0},
series = {Lecture Notes in Computer Science ({LNCS})},
pages = {183--187},
booktitle = {Provenance and Annotation of Data and Processes - International Provenance and Annotation Workshop (IPAW)},
publisher = {Springer International Publishing},
author = {Silva, Vítor and Souza, Renan and Camata, Jose and de Oliveira, Daniel and Valduriez, Patrick and Coutinho, Alvaro L. G. A. and Mattoso, Marta},
year = {2018},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-319-98379-0_15}
} |
| Parallel Execution of Workflows driven by Distributed Database Techniques R. Souza MSc Thesis Contest: Brazilian Symposium on Databases (SBBD), 2017. [C33][pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza_2017_msc_contest,
title = {Parallel Execution of Workflows driven by Distributed Database Techniques},
pdf = {https://scholar.google.com.br/scholar?oi=bibs&cluster=17975638527136409759&btnI=1&hl=en},
booktitle = {MSc Thesis Contest: Brazilian Symposium on Databases ({SBBD})},
author = {Souza, Renan},
year = {2017}
} |
| Tracking of online parameter fine-tuning in scientific workflows R. Souza, V. Silva, J. Camata, A. Coutinho, P. Valduriez, and M. Mattoso Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science (WORKS) workshop co-located with the ACM/IEEE International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC), 2017. [C34][online] [bibtex]@inproceedings{Souza2017Tracking,
location = {Denver, {CO}},
title = {Tracking of online parameter fine-tuning in scientific workflows},
booktitle = {Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science ({WORKS}) workshop co-located with the {ACM}/{IEEE} International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis ({SC})},
author = {Souza, Renan and Silva, Vítor and Camata, José and Coutinho, Alvaro and Valduriez, Patrick and Mattoso, Marta},
year = {2017},
url = {https://hal-lirmm.ccsd.cnrs.fr/lirmm-01620974}
} |
| Spark Scalability Analysis in a Scientific Workflow R. Souza, V. Silva, P. Miranda, A.A.B. Lima, P. Valduriez, and M. Mattoso Brazilian Symposium on Databases (SBBD), 2017. [C35][pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{Souza2017Spark,
title = {Spark Scalability Analysis in a Scientific Workflow},
pdf = {http://sbbd.org.br/2017/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2018/02/p288-293.pdf},
pages = {288--293},
booktitle = {Brazilian Symposium on Databases ({SBBD})},
author = {Souza, Renan and Silva, Vítor and Miranda, Pedro and Lima, Alexandre A B and Valduriez, Patrick and Mattoso, Marta},
year = {2017}
} |
| Building a question-answering corpus using social media and news articles P. Cavalin, F. Figueiredo, M.d. Bayser, L. Moyano, H. Candello, A. Appel, and R. Souza International Conference on Computational Processing of the Portuguese Language, 2016. [C36] [bibtex]@inproceedings{cavalin2016building,
title={Building a question-answering corpus using social media and news articles},
author={Cavalin, Paulo and Figueiredo, Flavio and de Bayser, Maíra and Moyano, Luis and Candello, Heloisa and Appel, Ana and Souza, Renan},
booktitle={International Conference on Computational Processing of the Portuguese Language},
pages={353--358},
year={2016}
} |
| Applying future Exascale HPC methodologies in the energy sector J.J. Camata, J.M. Cela, D. Costa, A.L.G.A. Coutinho, D. Fernández-Galisteo, R. Souza, and others Russian Supercomputing days, 2016. [C37][online] [pdf] [bibtex]@article{camata_applying_2016,
title = {Applying future Exascale {HPC} methodologies in the energy sector},
booktitle = {Russian Supercomputing days},
url = {https://upcommons.upc.edu/handle/2117/90905},
pages = {9--19},
author = {Camata, José J. and Cela, José M. and Costa, Danilo and Coutinho, Alvaro L. G. A. and Fernández-Galisteo, Daniel and Souza, Renan and others},
keywords = {Algorithms and architectures for advanced scientific computing, Àrees temàtiques de la {UPC}::Energies, Biomass, Energy sources, Exascale, Hidrocarburs, {HPC}, Hydrocarbon, Hydrocarbon processing, Supercomputadors, Wind energy},
year = {2016},
pdf = {https://upcommons.upc.edu/bitstream/handle/2117/90905/Applying%20future%20Exascale%20HPC%20methodologies%20in%20the%20energy%20sector.pdf}
} |
| Enhancing Energy Production with Exascale HPC Methods J. Camata, J.M. Cela, D. Costa, A.L.G.A. Coutinho, D. Fernández-Galisteo, C. Jimenez, V. Kourdioumov, M. Mattoso, R. Mayo-García, T. Miras, J.A. Moríñigo, J. Navarro, P.O.A. Navaux, D.D. Oliveira, M. Rodríguez-Pascual, V. Silva, R. Souza, and P. Valduriez CARLA: Latin American High Performance Computing Conference, 2016. [C38][doi] [online] [pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{camata:lirmm-01654914,
TITLE = {{Enhancing Energy Production with Exascale HPC Methods}},
author = {Camata, José and Cela, José M and Costa, Danilo and Coutinho, Alvaro L. G. A. and Fernández-Galisteo, Daniel and Jimenez, Carmen and Kourdioumov, Vadim and Mattoso, Marta and Mayo-García, Rafael and Miras, Thomas and Moríñigo, José A and Navarro, Jorge and Navaux, Philippe O A and De Oliveira, Daniel and Rodríguez-Pascual, Manuel and Silva, Vítor and Souza, Renan and Valduriez, Patrick},
url = {https://hal-lirmm.ccsd.cnrs.fr/lirmm-01654914},
booktitle = {{CARLA: Latin American High Performance Computing Conference}},
address = {Mexico City, Mexico},
publisher = {{Springer}},
volume = {Communications in Computer and Information Science},
number = {697},
pages = {233-246},
year = {2016},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-319-57972-6\_17},
pdf = {https://hal-lirmm.ccsd.cnrs.fr/lirmm-01654914/file/Enhancing%20Energy%20Production%20with%20Exascale%20HPC.pdf}
} |
| Online Input Data Reduction in Scientific Workflows R. Souza, V. Silva, A. Coutinho, P. Valduriez, and M. Mattoso Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science (WORKS) workshop co-located with the ACM/IEEE International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC), 2016. [C39][online] [bibtex]@inproceedings{Souza2016Online,
title = {Online Input Data Reduction in Scientific Workflows},
url = {https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/lirmm-01400538},
pages = {1--10},
booktitle = {Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science ({WORKS}) workshop co-located with the {ACM}/{IEEE} International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis ({SC})},
author = {Souza, Renan and Silva, Vítor and Coutinho, Alvaro and Valduriez, Patrick and Mattoso, Marta},
year = {2016}
} |
| Integrating Domain-data Steering with Code-profiling Tools to Debug Data-intensive Workflows V. Silva, L. Neves, R. Souza, A. Coutinho, D.D. Oliveira, and M. Mattoso Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science (WORKS) workshop co-located with the ACM/IEEE International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC), 2016. [C40] [bibtex]@inproceedings{Silva2016Integrating,
location = {Salt Lake City, {USA}},
title = {Integrating Domain-data Steering with Code-profiling Tools to Debug Data-intensive Workflows},
booktitle = {Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science ({WORKS}) workshop co-located with the {ACM}/{IEEE} International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis ({SC})},
author = {Silva, Vítor and Neves, Leonardo and Souza, Renan and Coutinho, Alvaro and Oliveira, Daniel De and Mattoso, Marta},
year = {2016},
keywords = {Provenance, Performance analysis, Scientific Workflow, Debugging}
} |
| Uma Abordagem para Publicação de Dados de Proveniência de Workflows Científicos na Web Semântica R. Castro, R. Souza, V. Silva, K. Ocaña, D. Oliveira, and M. Mattoso Brazilian Symposium on Databases (SBBD), 2015. [C41] [bibtex]@inproceedings{castro2015abordagem,
title={Uma Abordagem para Publicação de Dados de Proveniência de Workflows Científicos na Web Semântica},
author={Castro, Rachel and Souza, Renan and Silva, Vítor and Ocaña, Kary and Oliveira, Daniel and Mattoso, Marta},
booktitle={Brazilian Symposium on Databases ({SBBD})},
year={2015}
} |
| Applying data warehousing and big data techniques to analyze internet performance T. Barbosa, R. Souza, S. Cruz, M. Campos, and R.L. Cottrell International Conference on Internet Applications, Protocols, and Services, 2015. [C42][pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{barbosa2016applying,
title={Applying data warehousing and big data techniques to analyze internet performance},
author={Barbosa, TMS and Souza, Renan and Cruz, SMS and Campos, ML and Cottrell, R Les},
year={2015},
booktitle={International Conference on Internet Applications, Protocols, and Services},
pdf = {https://www.slac.stanford.edu/pubs/slacpubs/16250/slac-pub-16464.pdf}
} |
| Parallel Execution of Workflows Driven by a Distributed Database Management System R. Souza, V. Silva, D. Oliveira, P. Valduriez, A.A.B. Lima, and M. Mattoso ACM/IEEE International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC), 2015. [C43][online] [pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{Souza2015Parallel,
location = {Salt Lake City, {USA}},
title = {Parallel Execution of Workflows Driven by a Distributed Database Management System},
url = {http://sc15.supercomputing.org/sites/all/themes/SC15images/tech_poster/tech_poster_pages/post284.html},
pdf = {http://sc15.supercomputing.org/sites/all/themes/SC15images/tech_poster/poster_files/post284s2-file3.pdf},
pages = {1--3},
booktitle = {{ACM}/{IEEE} International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis ({SC})},
author = {Souza, Renan and Silva, Vítor and Oliveira, Daniel and Valduriez, Patrick and Lima, Alexandre A. B. and Mattoso, Marta},
year = {2015}
} |
| Linked open data publication strategies: Application in networking performance measurement data R. Souza, L. Cottrell, B. White, M.L. Campos, and M. Mattoso ASE BigData/SocialCom/CyberSecurity, Stanford, CA, 2014. [C44][pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{souza2014linked,
title={Linked open data publication strategies: Application in networking performance measurement data},
author={Souza, Renan and Cottrell, Les and White, Bebo and Campos, Maria L and Mattoso, Marta},
booktitle={ASE BigData/SocialCom/CyberSecurity, Stanford, CA},
pdf = {https://www.slac.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/getdoc/slac-pub-15950.pdf},
year={2014}
} |
Technical Reports 
| OLCF's Advanced Computing Ecosystem (ACE): FY25 Update for Ongoing Efforts B. Etz, S. Oral, R.F.D. Silva, R. Adamson, A. Alnajjar, T. Beck, A. Barker, M. Brim, P. Bryant, R. Souza, and others , 2025. [R1][doi] [online] [pdf] [bibtex]@techreport{etz2025olcf,
title={OLCF's Advanced Computing Ecosystem (ACE): FY25 Update for Ongoing Efforts},
author={Etz, Brian and Oral, Sarp and Ferreira Da Silva, Rafael and Adamson, Ryan and Alnajjar, Anees and Beck, Tom and Barker, Ashley and Brim, Michael and Bryant, Paul and Souza, Renan and others},
year={2025},
pdf={https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/3006499},
url={https://www.osti.gov/biblio/3006499},
doi={10.2172/3006499},
institution={Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)}
} |
| Workflows Community Summit 2024: Future Trends and Challenges in Scientific Workflows D. Bard, K. Chard, S.d. Witt, I.T. Foster, C. Goble, W. Godoy, J. Gustafsson, U. Haus, S. Hudson, L. Los, R. Souza, and others Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC), 2024. [R2][doi] [online] [pdf] [bibtex]@article{bard2024workflows,
title={Workflows Community Summit 2024: Future Trends and Challenges in Scientific Workflows},
author={Bard, Deborah and Chard, Kyle and de Witt, Shaun and Foster, Ian T and Goble, Carole and Godoy, William and Gustafsson, Johan and Haus, Utz-Uwe and Hudson, Stephen and Los, Laila and Souza, Renan and others},
year={2024},
pdf={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2410.14943},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.14943},
doi={https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2410.14943},
journal={Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC)}
} |
| Workflows Community Summit 2022: A Roadmap Revolution R.F.d. Silva, R.M. Badia, V. Bala, D. Bard, P. Bremer, I. Buckley, S. Caino-Lores, K. Chard, C. Goble, S. Jha, ..., R. Souza, and e. al. arXiv preprint Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC), 2023. [R3][doi] [online] [pdf] [bibtex]@article{da2023workflows,
title={Workflows Community Summit 2022: A Roadmap Revolution},
author={da Silva, Rafael Ferreira and Badia, Rosa M and Bala, Venkat and Bard, Debbie and Bremer, Peer-Timo and Buckley, Ian and Caino-Lores, Silvina and Chard, Kyle and Goble, Carole and Jha, Shantenu and ... and Souza, Renan and {et al.}},
journal={arXiv preprint Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC)},
doi={10.48550/arXiv.2304.00019},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.00019},
pdf={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.00019},
year={2023}
} |
| A Polystore Architecture Using Knowledge Graphs to Support Queries on Heterogeneous Data Stores L.G. Azevedo, R. Souza, E.F.d.S. Soares, R.M. Thiago, J.C.C. Tesolin, A.C. Oliveira, and M.F. Moreno arXiv preprint Databases (cs.DB), 2023. [R4][doi] [online] [pdf] [bibtex]@article{azevedo2023polystore,
title={A Polystore Architecture Using Knowledge Graphs to Support Queries on Heterogeneous Data Stores},
author={Azevedo, Leonardo Guerreiro and Souza, Renan and Soares, Elton F de S and Thiago, Raphael M and Tesolin, Julio Cesar Cardoso and Oliveira, Ann C and Moreno, Marcio Ferreira},
journal={arXiv preprint Databases (cs.DB)},
doi={10.48550/arXiv.2308.03584},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.03584},
pdf={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2308.03584},
year={2023}
} |
| Workflows Community Summit: Advancing the State-of-the-art of Scientific Workflows Management Systems Research and Development R.F.d. Silva, H. Casanova, K. Chard, ..., R. Souza, and e. al. arXiv preprint Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC), 2021. [R5][online] [pdf] [bibtex]@inproceedings{rafael_2021_wf_summit,
title={Workflows Community Summit: Advancing the State-of-the-art of Scientific Workflows Management Systems Research and Development},
author={da Silva, Rafael Ferreira and Casanova, Henri and Chard, Kyle and ... and Souza, Renan and {et al.}},
journal={arXiv preprint Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC)},
pdf = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2106.05177.pdf},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.05177},
pages={1--24},
year={2021}
} |
| A Hybrid Architecture for Multi-party Conversational Systems M.G.d. Bayser, P. Cavalin, R. Souza, A. Braz, H. Candello, C. Pinhanez, and J. Briot arXiv preprint Computation and Language (cs.CL), 2017. [R6][online] [pdf] [bibtex]@article{de2017hybrid,
title={A Hybrid Architecture for Multi-party Conversational Systems},
author={de Bayser, Maira Gatti and Cavalin, Paulo and Souza, Renan and Braz, Alan and Candello, Heloisa and Pinhanez, Claudio and Briot, Jean-Pierre},
journal={arXiv preprint Computation and Language (cs.CL)},
pdf = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.01214.pdf},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.01214},
pages={1--40},
year={2017}
} |
Patents 
| Shortened narrative instruction generator for software code change M.A.S. Netto, L.C.V. Real, B. Silva, and R. Souza US Patent App. 17/819,025, 2024. [P1][online] [bibtex]@misc{netto2024shortened,
title={Shortened narrative instruction generator for software code change},
author={Netto, Marco Aurelio Stelmar and Real, Lucas Correia Villa and Silva, Bruno and Souza, Renan},
year={2024},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US20240053980A1/en},
note={US Patent App. 17/819,025}
} |
| Data transformation for acceleration of context migration in interactive computing notebooks L.C.V. Real, R.L.D.F. Cunha, R. Souza, and M.A.S. Netto Granted, US Patent App. 17/683,279, 2023. [P2][online] [bibtex]@misc{real2023data,
title={Data transformation for acceleration of context migration in interactive computing notebooks},
author={Real, Lucas Correia Villa and Cunha, Renato Luiz De Freitas and Souza, Renan and Netto, Marco Aurelio Stelmar},
year={2023},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US20230012543A1/en},
note={Granted, US Patent App. 17/683,279}
} |
| Remotely healing crashed processes M.A.S. Netto, B. Silva, R.L.D.F. Cunha, R. Souza, and L.C.V. Real US Patent App. 17/480,087, 2023. [P3][online] [bibtex]@misc{netto2023remotely,
title={Remotely healing crashed processes},
author={Netto, Marco Aurelio Stelmar and Silva, Bruno and Cunha, Renato Luiz De Freitas and Souza, Renan and Real, Lucas Correia Villa},
year={2023},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US20230088318A1/en},
note={US Patent App. 17/480,087}
} |
| Program context migration L.C.V. Real, M.A.S. Netto, R.L.D.F. Cunha, R. Souza, and A. Braz Granted, US Patent App. 17/216,817, 2022. [P4][online] [bibtex]@misc{real2022program,
title={Program context migration},
author={Real, Lucas Correia Villa and Netto, Marco Aurelio Stelmar and Cunha, Renato Luiz De Freitas and Souza, Renan and Braz, Alan},
year={2022},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US20220318049A1/en},
note={Granted, US Patent App. 17/216,817}
} |
| Asset identification for collaborative projects in software development L.C.V. Real, R.L.D.F. Cunha, M.N.d. Santos, and R. Souza Granted, US Patent App. 17/118,646, 2022. [P5][online] [bibtex]@misc{real2022asset,
title={Asset identification for collaborative projects in software development},
author={Real, Lucas Correia Villa and Cunha, Renato Luiz De Freitas and dos Santos, Marcelo Nery and Souza, Renan},
year={2022},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US11650812/en},
note={Granted, US Patent App. 17/118,646}
} |
| Model Document Creation in Source Code Development Environments using Semantic-aware Detectable Action Impacts A.P. Appel, C.R.L.D. Freitas, R. Souza, C.R.D.A. Mendes, A. Vital, N. Dos, S. Marcelo, M.A.S. Netto, P.B. Avegliano, and C. Villas US Patent App. 17/353,731, 2022. [P6][online] [bibtex]@misc{appel2022model,
title={Model Document Creation in Source Code Development Environments using Semantic-aware Detectable Action Impacts},
author={Appel, Ana Paula and De Freitas, Cunha Renato Luiz and Souza, Renan and Mendes, Carlos Raoni De Alencar and Vital, Ashton and Dos, Nery and Marcelo, Santos and Stelmar Netto, Marco Aurelio and Avegliano, Priscilla Barreira and Villas, Costa},
year={2022},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US20220405065A1/en},
note={US Patent App. 17/353,731}
} |
| Metadata-based scientific data characterization driven by a knowledge database at scale R. Souza, R. Mozart, F.R.D. Silva, A. Vital, and V.T.d. Silva Granted, US Patent App. 16/527,546, 2021. [P7][online] [bibtex]@misc{souza2021metadata,
title={Metadata-based scientific data characterization driven by a knowledge database at scale},
author={Souza, Renan and Mozart, Reinaldo and Da Silva, Ferreira Rodrigo and Vital, Ashton and Silva, Viviane Torres da},
year={2021},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US11494611/en},
note={Granted, US Patent App. 16/527,546}
} |
| Continuous storage of data in a system with limited storage capacity L.C.V. Real, M.N.d. Santos, and R. Souza Granted, US Patent App. 16/678,375, 2021. [P8][online] [bibtex]@misc{real2021continuous,
title={Continuous storage of data in a system with limited storage capacity},
author={Real, Lucas Correia Villa and dos Santos, Marcelo Nery and Souza, Renan },
year={2021},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US11221925/en},
note={Granted, US Patent App. 16/678,375}
} |
| Creating coordinated multi-chatbots using natural dialogues by means of knowledge base M.G.D. Bayser, A. Braz, P.R. Cavalin, F. Figueiredo, and R. Souza Granted, US Patent App. 15/217,660, 2018. [P9][online] [bibtex]@misc{de2018creating,
title={Creating coordinated multi-chatbots using natural dialogues by means of knowledge base},
author={De Bayser, Maira Gatti and Braz, Alan and Cavalin, Paulo Rodrigo and Figueiredo, Flavio and Souza, Renan},
year={2018},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US20180025726A1/en},
note={Granted, US Patent App. 15/217,660}
} |
| System and method for managing artificial conversational entities enhanced by social knowledge A. Braz, P.R. Cavalin, F. Figueiredo, M.G.D. Bayser, and R. Souza Granted, US Patent App. 15/265,615, 2018. [P10][online] [bibtex]@misc{braz2018system,
title={System and method for managing artificial conversational entities enhanced by social knowledge},
author={Braz, Alan and Cavalin, Paulo Rodrigo and Figueiredo, Flavio and De Bayser, Maira Gatti and Souza, Renan},
year={2018},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US10599644/en},
note={Granted, US Patent App. 15/265,615}
} |
| Predicting user question in question and answer system A.P. Appel, A.G. Leal, and R. Souza Granted, US Patent App. 15/171,055, 2017. [P11][online] [bibtex]@misc{appel2017predicting,
title={Predicting user question in question and answer system},
author={Appel, Ana P and Gama Leal, Andre and Souza, Renan},
year={2017},
url={https://patents.google.com/patent/US11687811B2/en},
note={Granted, US Patent App. 15/171,055}
} |